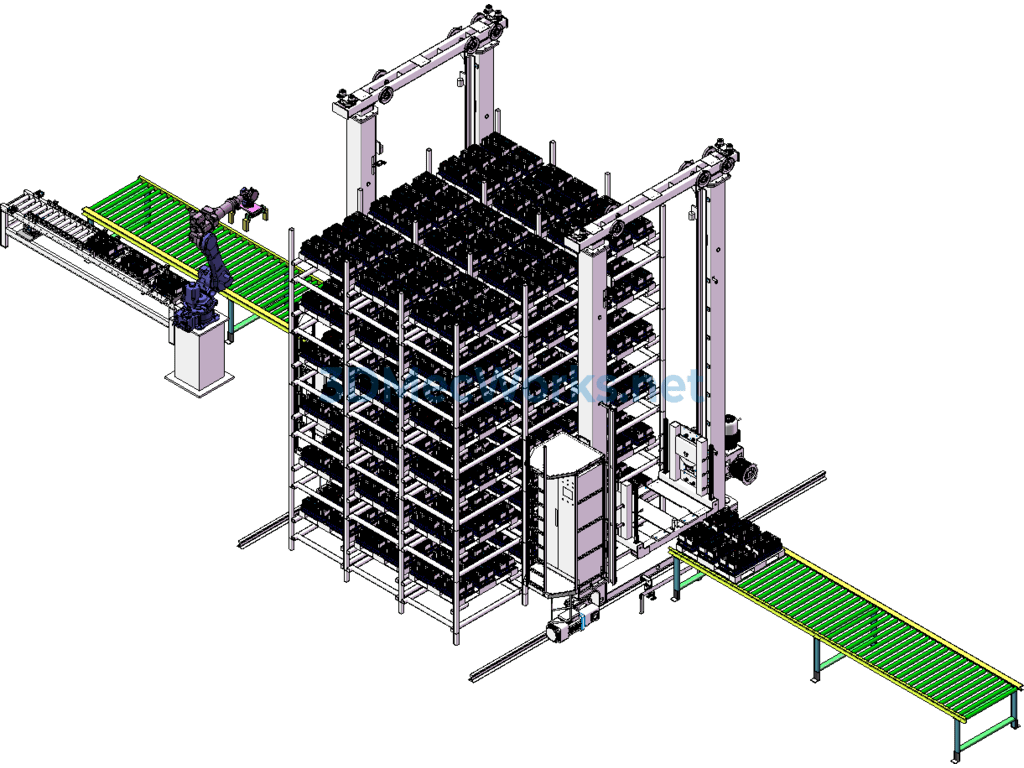
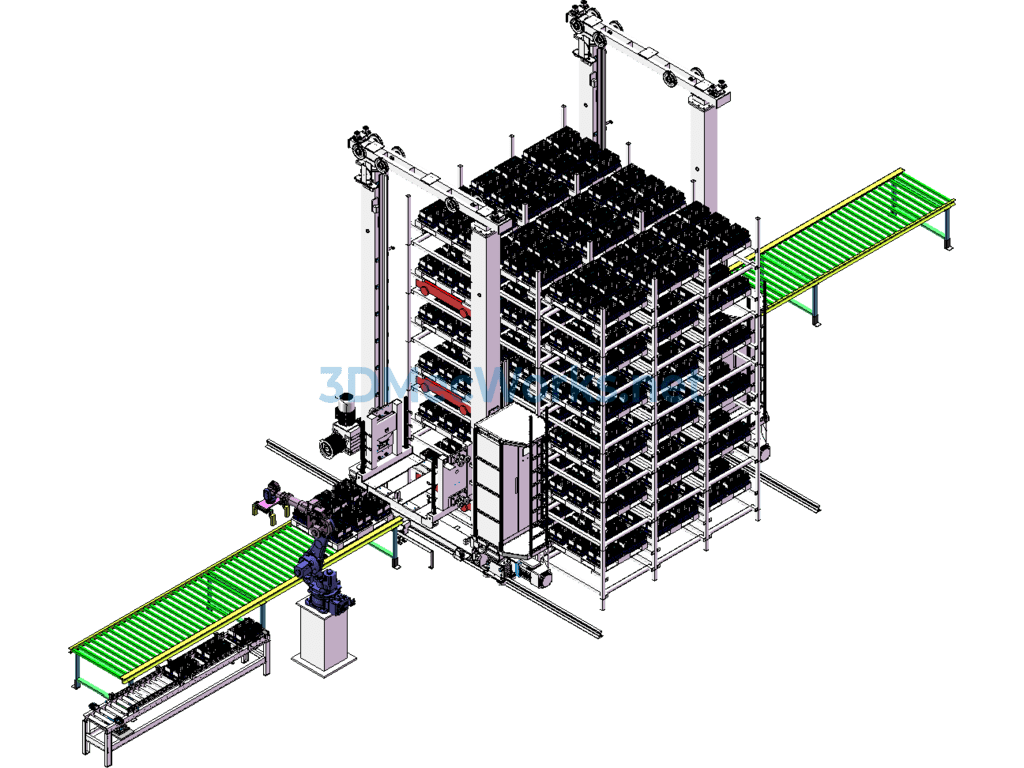
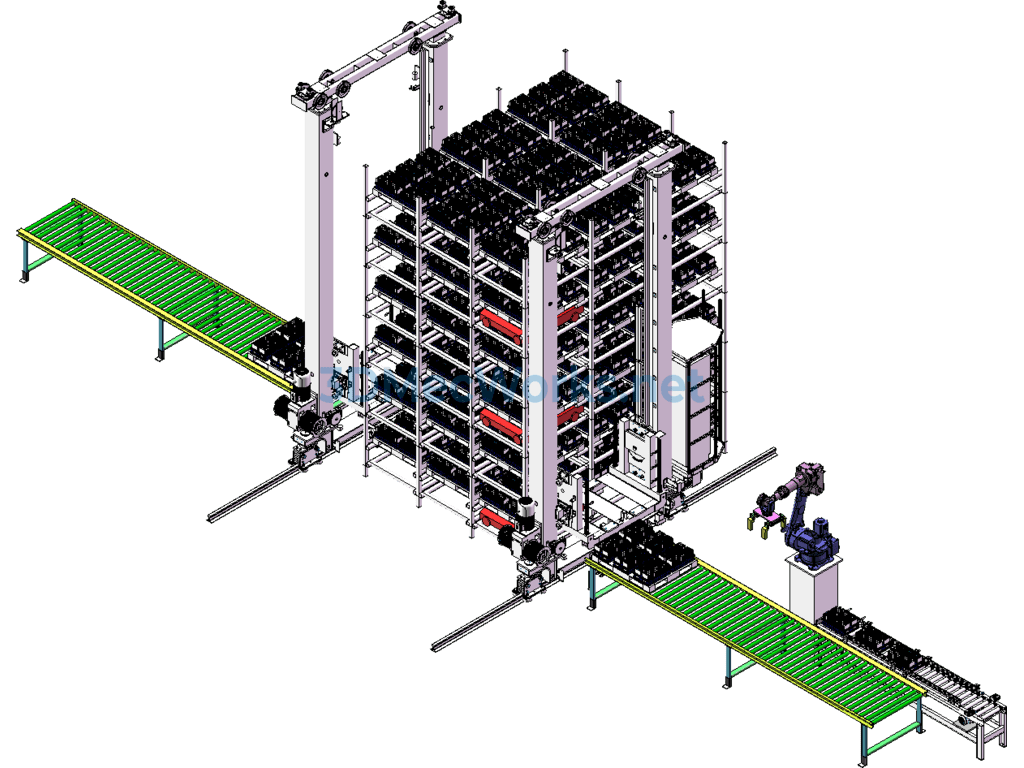
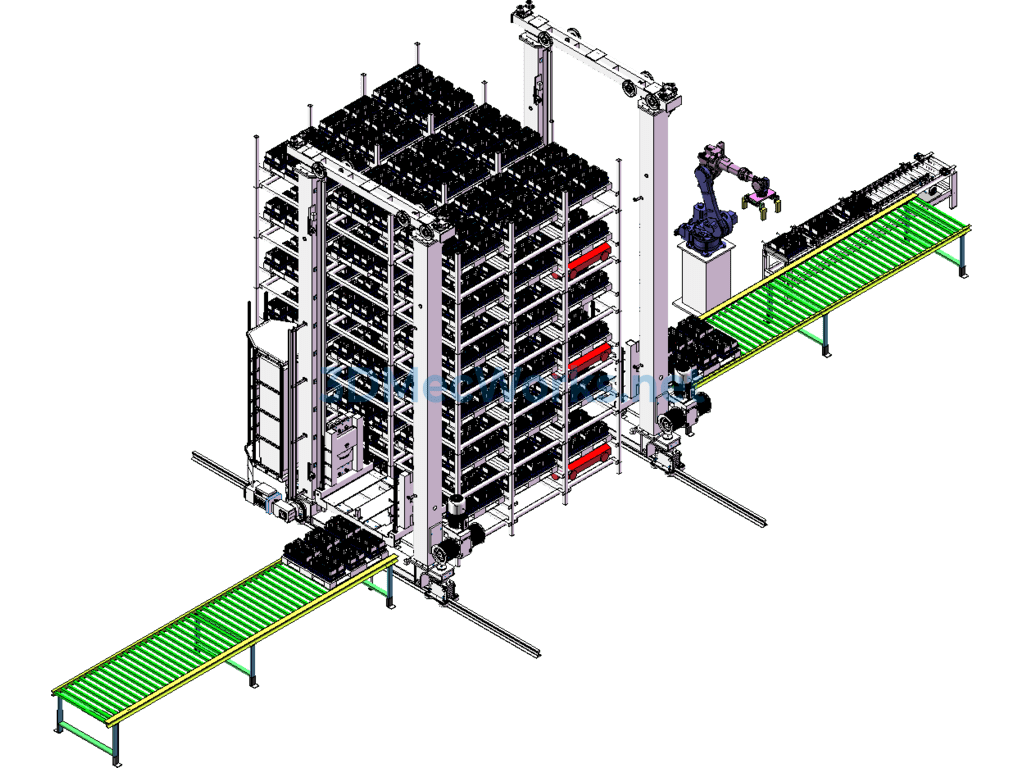
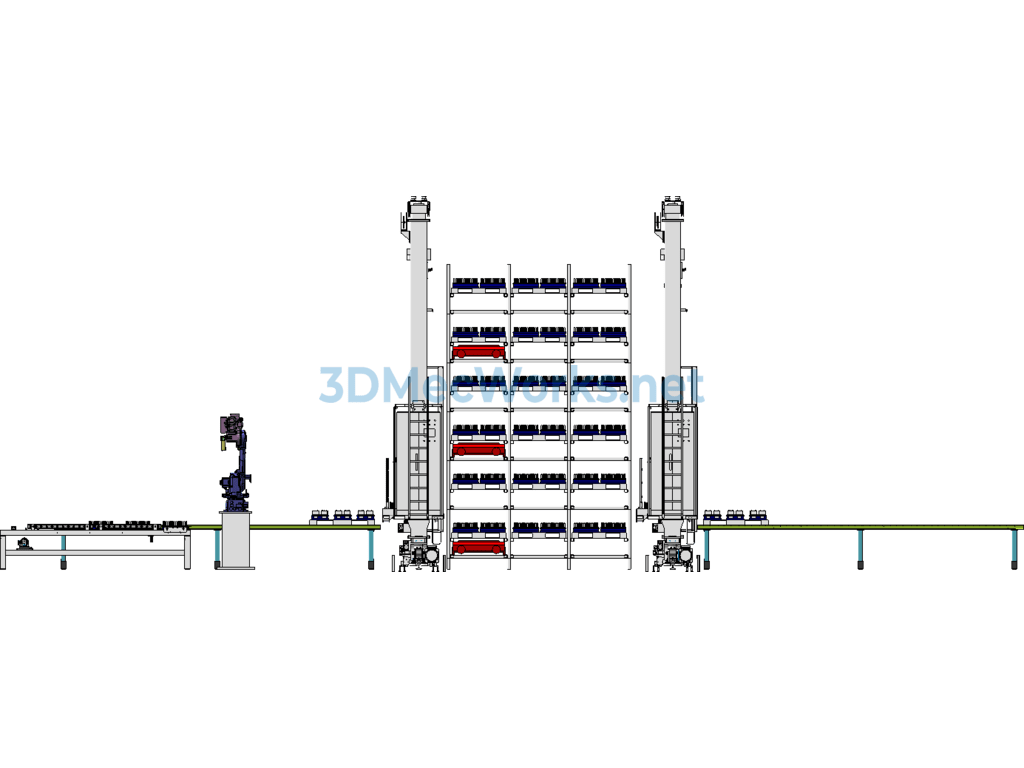
The model is an application for the entry and exit of lithium battery cells for electric vehicles in a three-dimensional warehouse. The cells are placed in grooves within a material frame that moves along a roller conveyor line to the grasping position of robot MH110. The robot then stacks the material frame on a 1200×1000 pallet located on another conveyor line. After the pallet is fully stacked, the automated warehouse stacker shuttle transfers the loaded pallet into the three-dimensional warehouse.
The four-way RGV in the warehouse can move in four directions within the three-dimensional warehouse, carrying pallets and materials in four directions, moving targets to specified locations in coordination with the stacker shuttle. The stacker shuttle can transfer targets between different levels of the automated storage.
This type of automated warehouse is a new form of storage, where the stacker shuttle can also be replaced by several elevators.
This model is merely a 3D data model and does not guarantee completely accurate dimensions for physical objects. The robot model is the YASKAWA MH110, a six-axis articulated robot with a payload of 110kg and a reach of 2236mm. The model is primarily used for creating robotic application solutions, application demonstrations, and simulations. It can also be used as material for 3D printing and may require post-processing. The attachment provides files in SolidWorks 2016 format, as well as STP and IGS files.
The models involved in industrial robots are three-dimensional models of industrial serial articulated robots, with the SolidWorks version being 2016. The position and range of motion for each axis are set according to parameters provided by the manufacturer. The reachable domain of the robot is where the flange center at the end of the robot can reach. In SolidWorks 2016 and later versions, you can open the assembly file attachment and drag any part of the robot (except for the base) with the mouse to illustrate the robot’s work range.
Section 1: How to Assemble and Customize the 3D Model
If the top-level assembly file is A.asm, then the robot attachment is a sub-assembly B.asm under A.asm. If a gripper is installed at the end of the robot, and it has no movable parts internally, install the gripper directly on the end flange. If the gripper has movable parts and you want to demonstrate them, define the gripper into several parts according to their movement range and size, and install them onto B.asm sequentially.
Section 2: How to Freely Drag the Robot Model in the Assembly
After assembling the top-level assembly A.asm according to the above rules, open the assembly and right-click properties in the feature tree. In the properties tab, select ‘Solve as Flexible’ in the lower right corner to freely move the robot’s joints and gripper in A.asm, facilitating the display of the reachable domain and details from different angles. Since the ‘Solve as Flexible’ function is resource-intensive, turn it off when not in use.
Section 3: Introduction to Main Parameters of the Model
The model mainly includes three parts: the length of the robot’s axes, the installation method of axes, and the movement angle size of the axes. The length and appearance of the axes are designed and determined by the robot company. The installation method and movement angle size are defined and constrained according to parameters provided by the robot company (latest version).
Ps1: Model Usage Notice. When the robot axes move to the limit position, forcibly dragging towards the limit with the mouse may cause the model to skip the restricted movement area to an unrestricted area. Particularly for axis J1, if the restricted area is small or can rotate beyond ±180 degrees, axis J1 can rotate continuously in a circle. Use caution by dragging the axes slightly. Once reaching a limit, a pause can be felt. Continuing will move into the restricted active area. Similar situations might occur for other axes, which is a software bug or undefined condition, similar to a singularity in robots.
PS2: The attachments provide standard format STP-AP214 files for users with SolidWorks versions below 2016 or other 3D software, allowing them to set the model according to the parameters in the attachments.
PS3: The model’s PRT files and parameters are sourced from publicly available information from the robot company. This model is for learning and demonstration purposes only. For industrial design or on-site production, please contact the robot supplier to verify the model’s dimensions and parameters carefully.
Specification: Rgv Four-Way Movable Three-Dimensional Warehouse Mh110 Robot Automation Palletizing Lithium Battery Cell Cell
|
User Reviews
Be the first to review “Rgv Four-Way Movable Three-Dimensional Warehouse Mh110 Robot Automation Palletizing Lithium Battery Cell Cell”
You must be logged in to post a review.





There are no reviews yet.