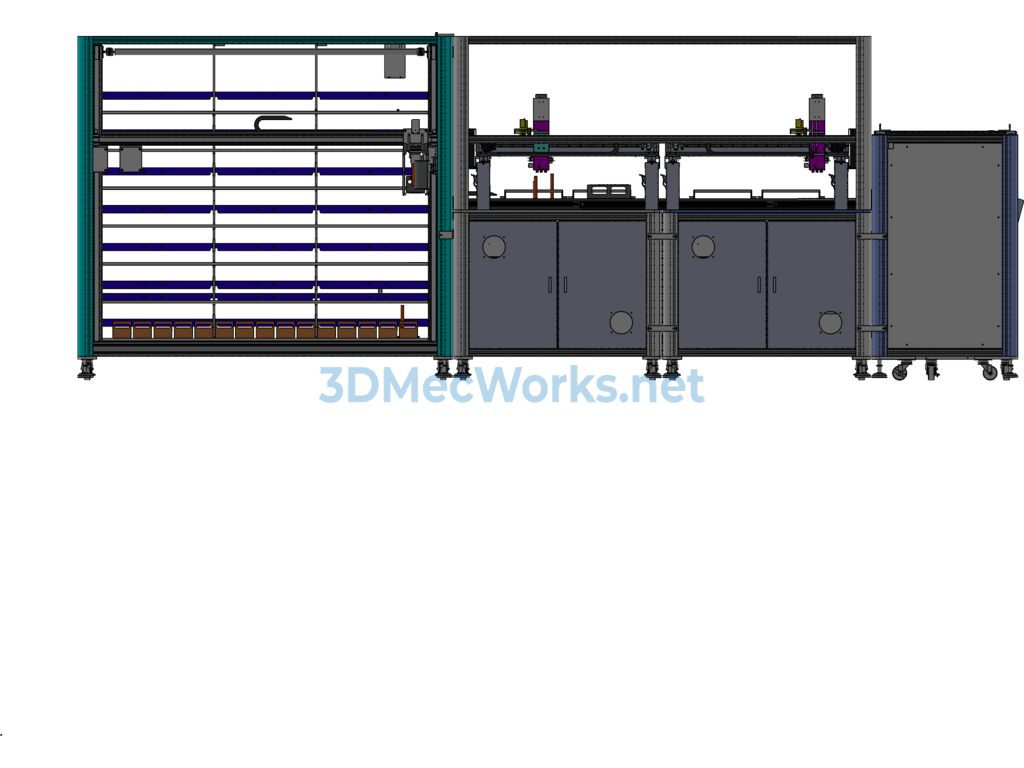
1. Standby: The manipulator is in a safe position with no conflicts with any of the modules; Cylinder, conveyor belt, tag printer, labeling machine, camera, elevator, standby;
2. Preparation: (Empty tube racks are placed properly, loading tube cart carries 10 tube racks to the designated position and is locked, empty collecting rack cart is pushed to designated position and locked, achieving required positioning accuracy) Sensors in various parts report status to indicate availability;
3. Scanning fraction racks: (Manually access the main control program, submit instrument number) The main program sends the number of fraction racks (loading racks) and action instructions. The manipulator moves, activates vision recognition installed on the Z-axis, scans QR codes on each fraction rack, and uploads data to the main program;
4. Verification: (The main program checks the fraction rack numbers with the sample selection table, after verification) The sample selection table is sent to the master of platform 2, issuing sample selection instructions;
5. Ejecting empty racks: The empty rack cylinder acts, ejecting a row of 7 empty tube racks onto the conveyor belt, the cylinder returns, and the upper rack slides down the slope; The conveyor belt moves a fixed length to transport the empty rack to the sample selection position, with vision for accurate positioning; (At this time, the empty rack cylinder operates, pushing out a new batch of empty tube racks)
6. Sample selection & labeling: Based on the sample selection table data (including source and target position data of target tubes), the manipulator sequentially selects samples, moves above the target tube, descends, grabs the tube, rises about 18cm, moves above the target position, and releases; The corners and centers of each loading and collecting tube rack must be accurately positioned;
6.1 For the first tube of each sample type, label it, the manipulator moves to the designated position (labeling machine), rotates and applies the label (labeling time coincides with tube selection, labeled awaiting tubes to pass over for labeling);
6.2 When target tubes (non-labeling tubes) are adjacent, both grippers simultaneously grab, transfer to target position, and release; If not adjacent, only one gripper works, transferring one tube at a time;
6.3 Tubes are in two models, 12.2*15cm and 18*15cm, grippers must be compatible with both specifications;
7. Conveyance: After selecting a sample, the conveyor belt advances a certain distance (based on how many tube racks are used, the target rack moves to the sample selection position), vision positioning occurs for new sample collection and transfer; Every time the liftable conveyor reaches 10 tube racks, based on system program data, the elevator runs to a designated level, the loader pushes the 10 tube racks one by one to specified positions, the elevator returns to normal height (the fixed-height conveyor temporarily does not convey samples, or protection devices are added);
8. Empty rack cylinder: When a stack of empty tube racks is used up, sensors send a signal to accordingly adjust the travel of the cylinder;
9. Collecting rack: When a layer of the collecting rack is fully stacked and there are more samples to be placed on this layer, an alarm reminds for replacement, after replacement, the layer’s data is reset, and the interrupted work continues;
10. Tube rack filling function: Change the empty rack to a 16*6 hole tube rack, change the loading tube cart to an empty tube dispensing device, the conveyor belt moves the empty rack to the appropriate position, stops, visual recognition for positioning, the manipulator picks each ejected tube one by one, visually checks for damage, discards it into the waste tube box if damaged, otherwise fills it into the tube rack; When the rack is full, move the conveyor belt, transfer to the storage rack via the elevator and cylinder. Initially, tube racks do not allow lateral movement, manual lifting and lowering is required.
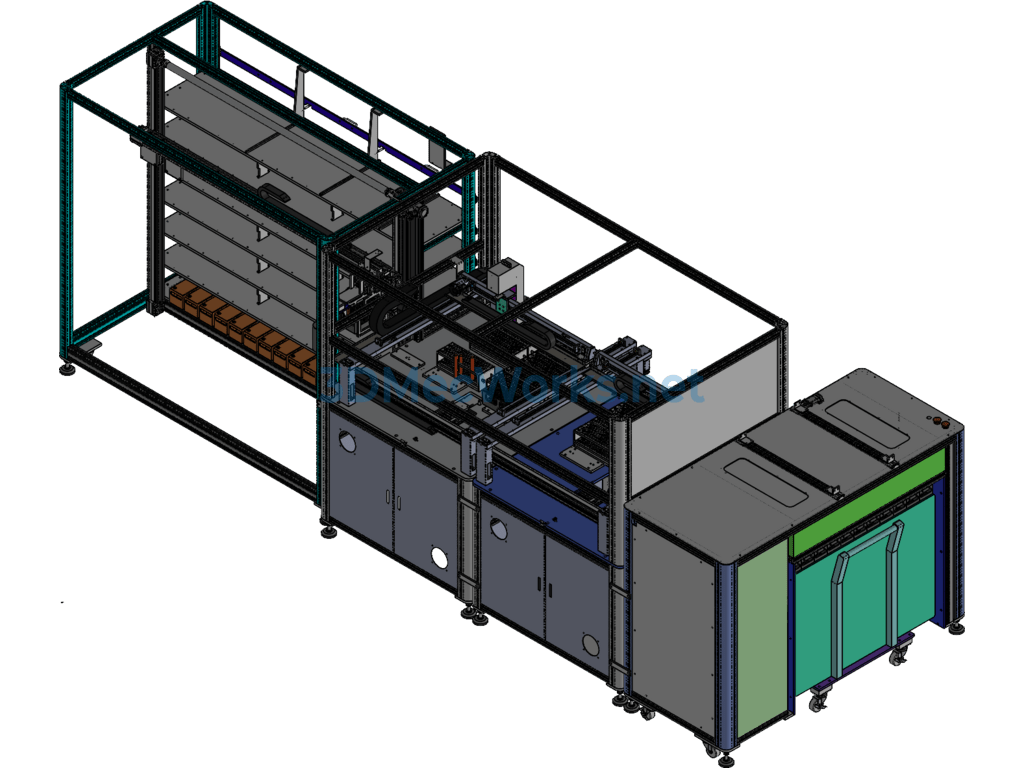
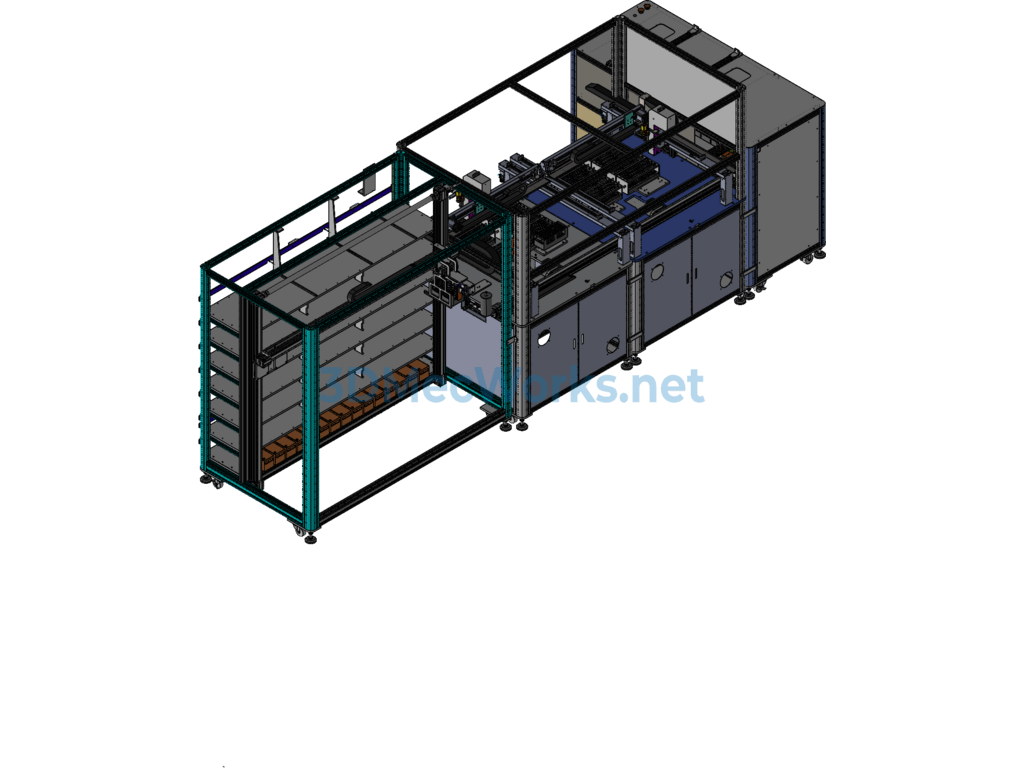
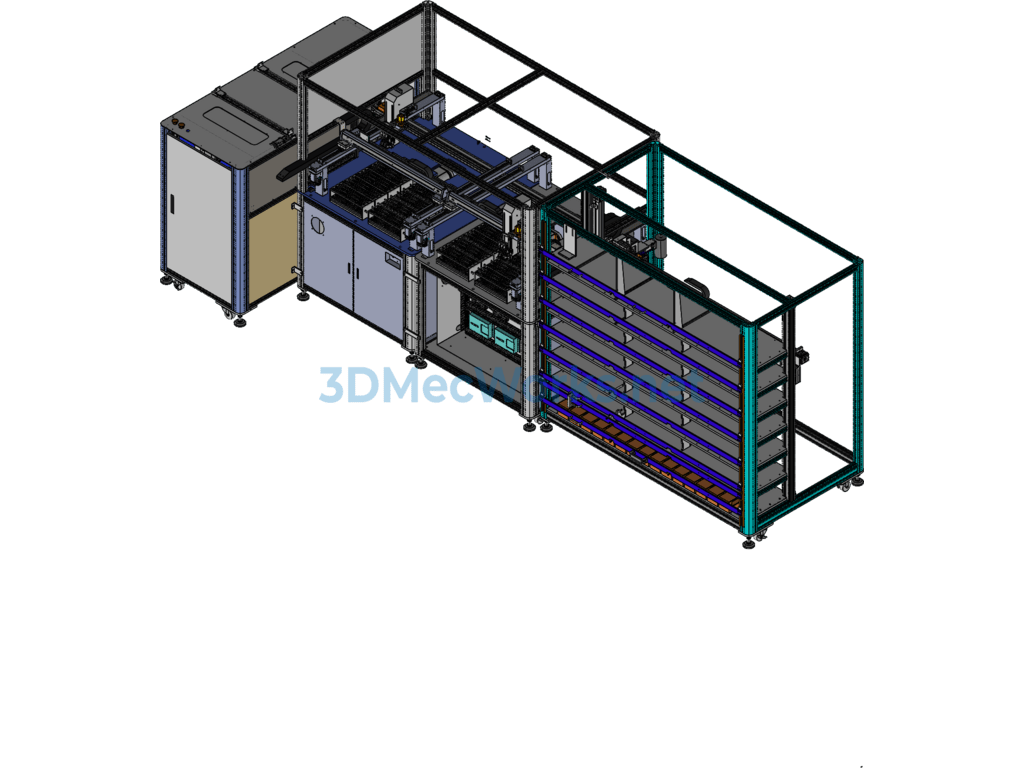
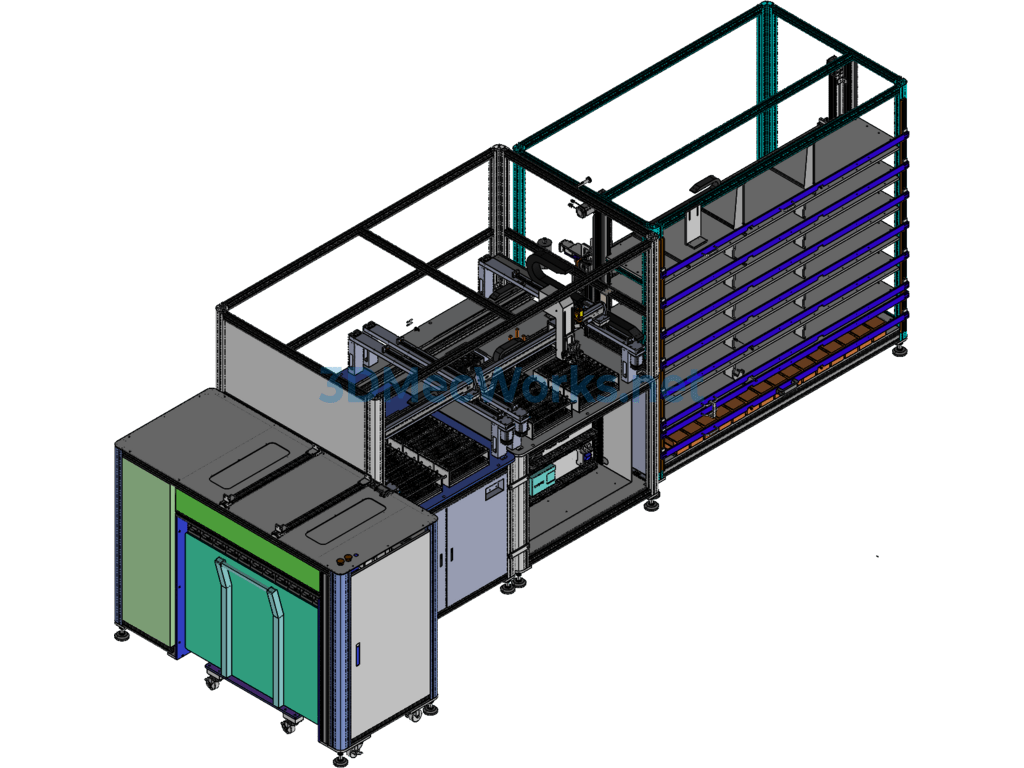
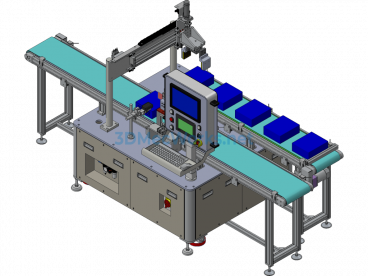
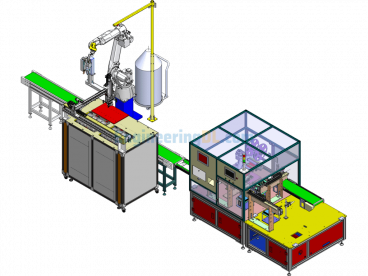
Specification: Medical Test Tube Sampling Machine
|
User Reviews
Be the first to review “Medical Test Tube Sampling Machine”
You must be logged in to post a review.



There are no reviews yet.