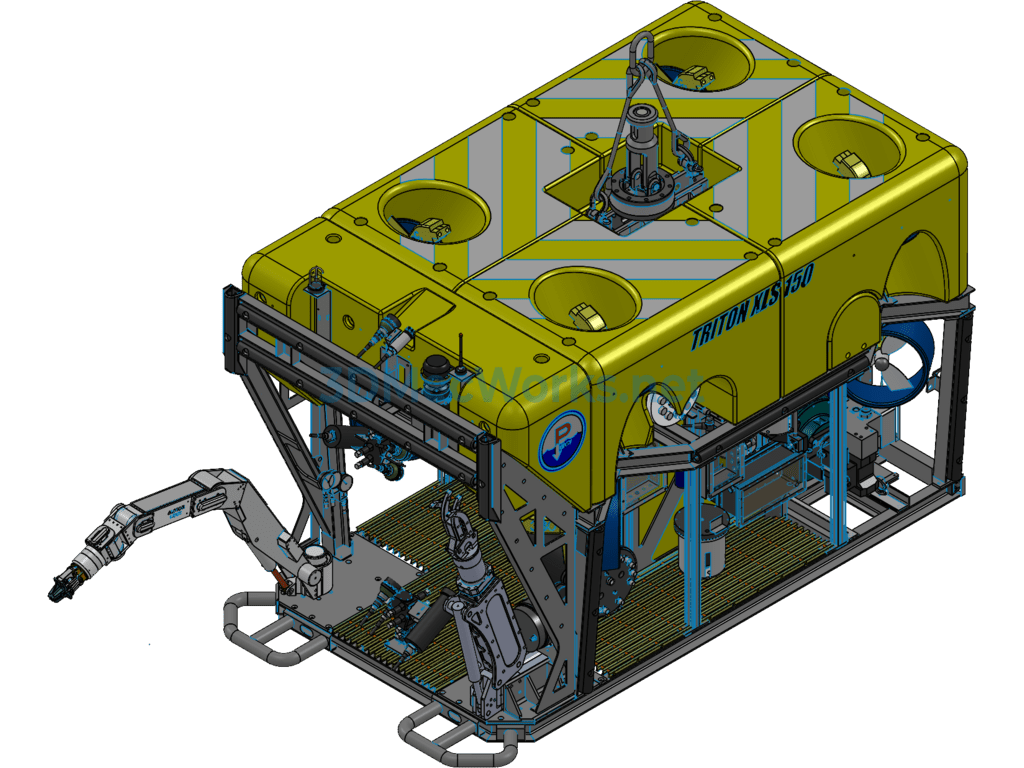
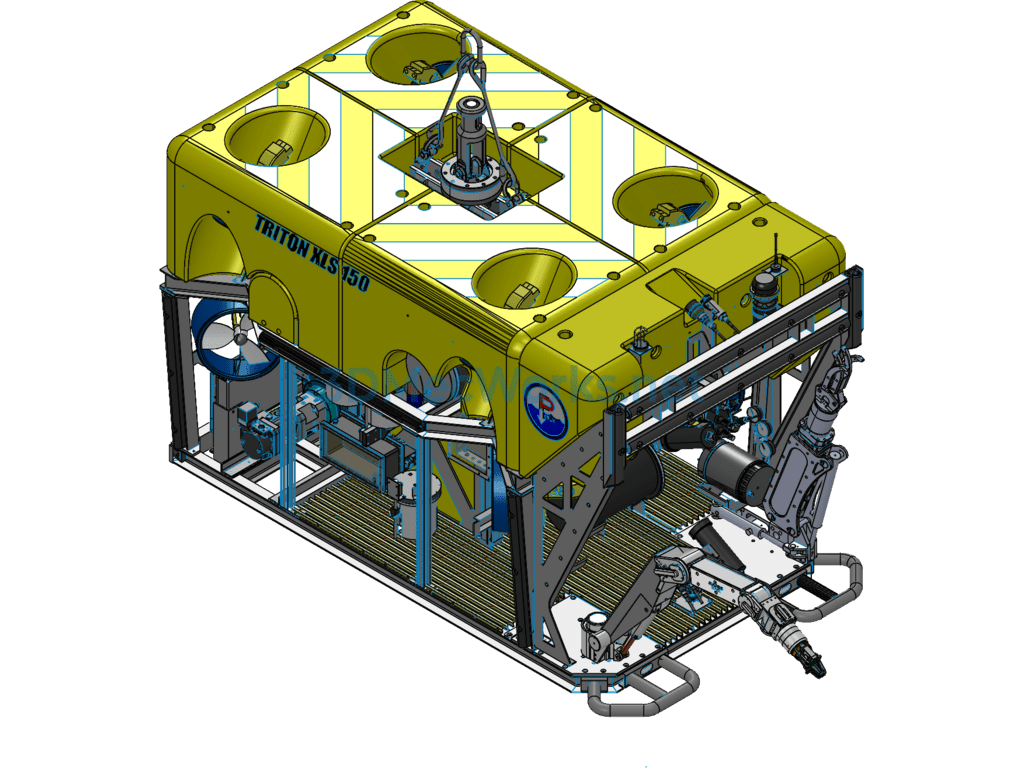
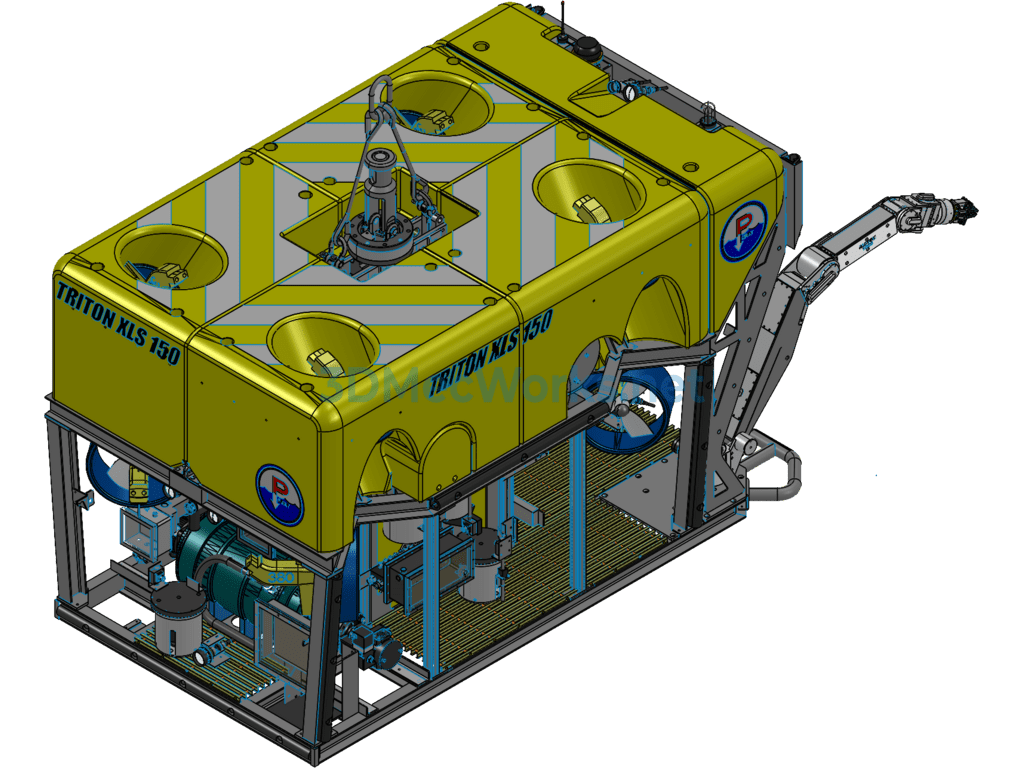
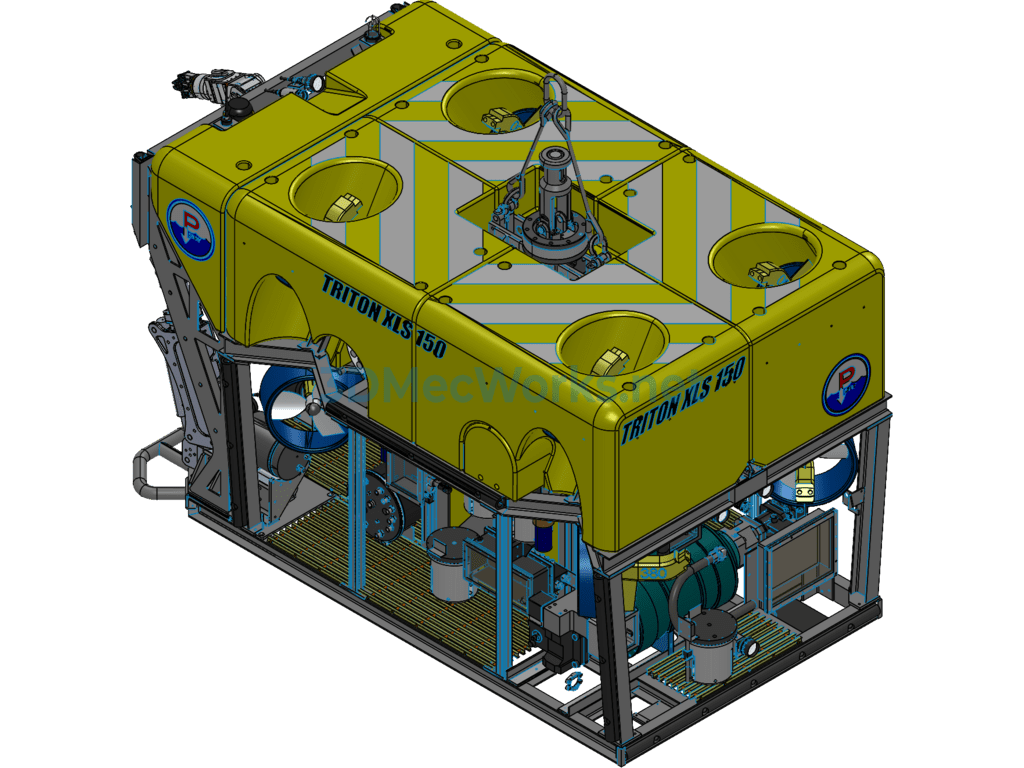
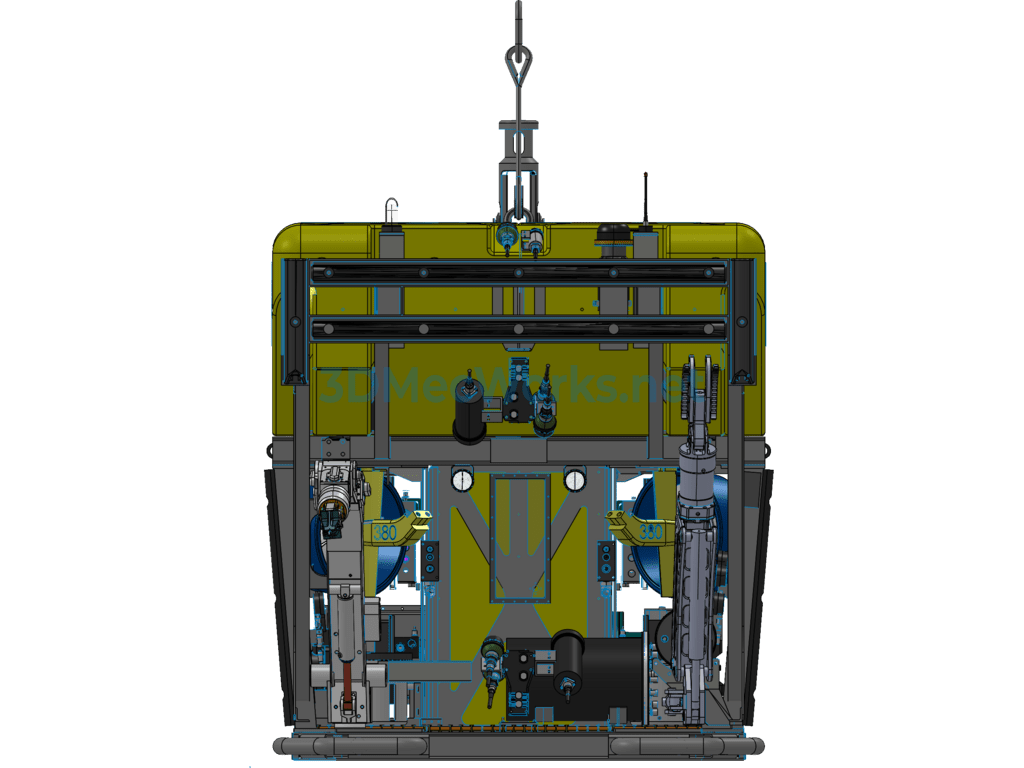
This underwater robot (Remotely Operated Vehicle, ROV) 3D model consists of the following system components: power thrusters, remote electronic communication devices, black-and-white or color cameras, a camera tilt gimbal, user peripheral sensor interfaces, a real-time online display unit, navigation and positioning devices, an autopilot navigation unit, auxiliary lighting, and a Kevlar neutral buoyancy tow cable. An ROV capable of diving deeper than 1000 meters is referred to as a deep-sea ROV, mainly used for deep-sea exploration and scientific research tasks. This model is from the XLS series by the American company DSSI, with a maximum diving depth of 2500 meters. The detection system primarily includes a seven-function mechanical arm, a five-function mechanical arm, one camera, one photograph camera, and various sensors. It also features an independent propulsion system.
A Remotely Operated Vehicle, also called an underwater robot, is a robot used for extreme operations underwater. It can dive into the water to perform certain tasks in place of humans and is also known as a submersible. Given the harsh and dangerous underwater environment and the limited diving depth for humans, underwater robots have become essential tools for ocean development. Remotely Operated Vehicles mainly include cable-controlled ROVs and cable-free ROVs. Cable-controlled ROVs are further divided into self-propelled, towable, and those capable of crawling on seabed structures.
Specification: Underwater Robot (remotely Operated Vehicle)
|
User Reviews
Be the first to review “Underwater Robot (remotely Operated Vehicle)”
You must be logged in to post a review.




There are no reviews yet.